Every RCM leader knows that without a set of KPIs you are flying blind. The first of these measures is Days in Accounts Receivable.
Why is it important?
You have to know how fast you are turning receivables into cash. It’s a quick indicator how well accounts are moving from admission to payment.
What’s the calculation?
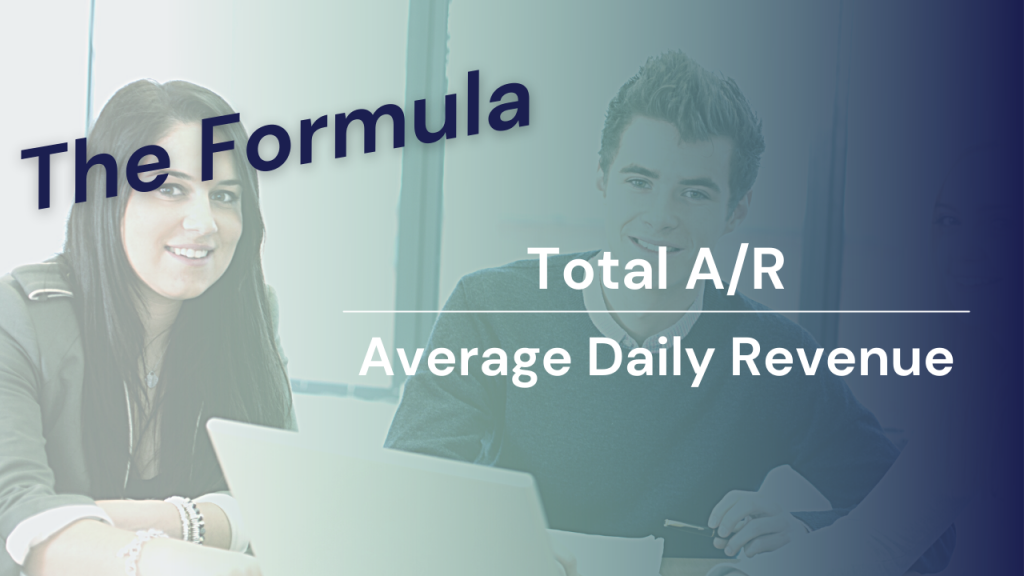
Average Daily Revenue is usually based on the most recent 3 Months (90 days). One can use gross revenue or more commonly, if your systems can account for the deductions in a timely manner, use net revenue (revenue that is net of credit balances, allowances for noncollectable accounts, discounts for charity care, and contractual allowances for third-party payers).
What is the benchmark?
Now that depends. If you have an older system bogged down with manual processes along with slow remits from payers, your days will naturally be higher. If you have newer systems and finely tuned automated processes with payers that remit in a timely manner, it’s possible to reach day in the mid 30’s and maybe even lower.
Knowing what your baseline is helps you know where you make an impact and when something is holding up your revenue.
How often should I update?
Now you will see this on the monthly financial reports provided by your finance department to leadership. However, AR days should be used as a daily operations indicator so you can catch as quickly as possible when the trend moves in the wrong direction and apply mitigation tactics as soon as possible.
Where do I get my data?
The finance department is going to use the Income Statement and Balance Sheet for the monthly reports. For daily tracking, your practice management system should have a report(s) that will provide total AR and daily revenue. You might get lucky and you’ll find a daily admin report that can be emailed to you each morning.
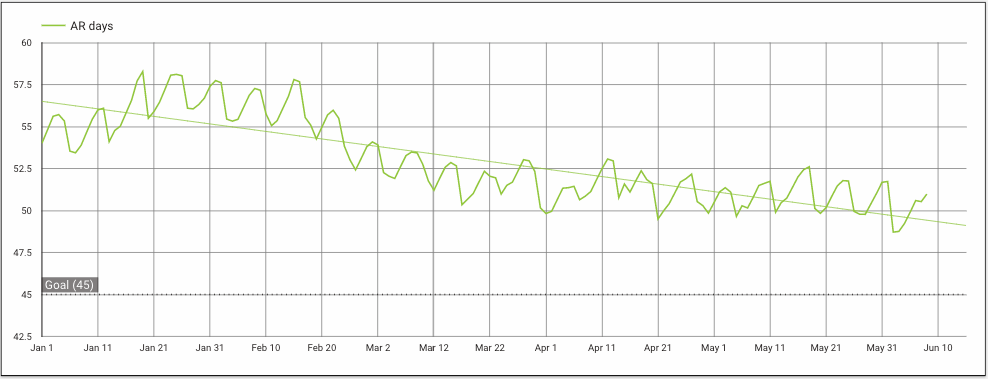
What does it look like?
What else?
There are related indicators I will be covering soon:
1. DNFB
2. Billed Days
3. Days on Hold
These indicators help drill down to specific areas that need attention. The above list will become active links when the articles are available.

